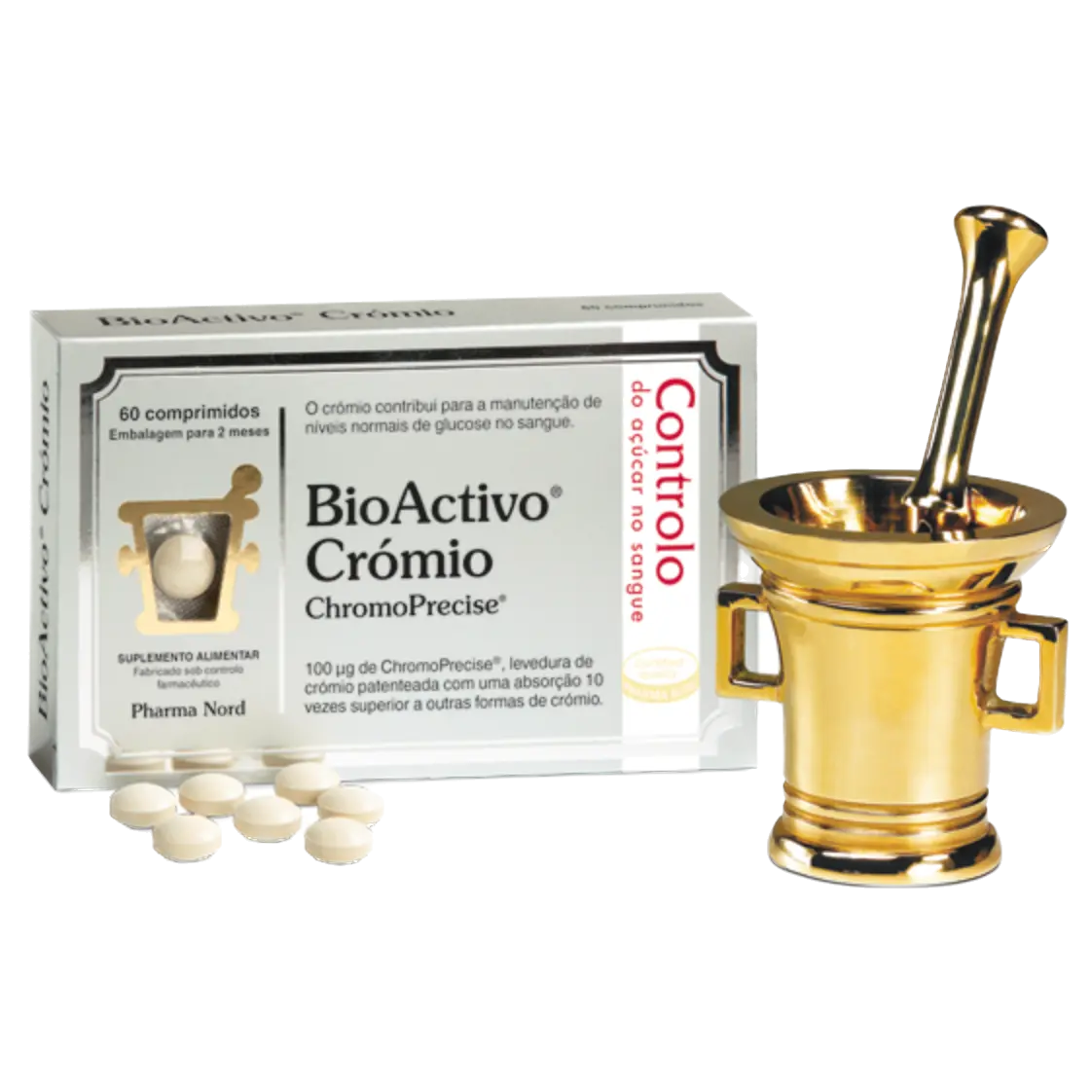
BioActivo Cromo 60cap - Pharma Nord
€18,70 EUR
Unit price
/
Unavailable
BioActivo Cromo 60cap - Pharma Nord is backordered and will ship as soon as it is back in stock.
Description
Description
BioActive Chromium
Vegan
Vegetarian
Vegetarian
- Organic chromium produced with chromium yeast
- High bioavailability
- Helps maintain normal blood glucose levels
- Contributes to normal macronutrient metabolism
- Manufactured under pharmaceutical control in Denmark
- Scientifically tested
Bioactive Chromium 60caps - Pharma Nord
What is BioActivo Chromium?
Each BioActivo Cromo tablet contains 100 micrograms of elemental chromium. The chromium used in BioActivo Cromo is organically bound, that is, it is bound to a yeast and amino acids (chromium yeast). It is highly absorbed by the body, 10 times greater than other approved chromium sources. BioActivo Cromo is produced with a patented chromium source called ChromoPrecise®, a chromium yeast specifically developed to provide excellent bioavailability. This specific chromium source is manufactured according to the strictest control standards (GMP standards used by the pharmaceutical industry) to ensure the efficacy and safety of the preparations, based on exhaustive documentation.
What is chromium?
Chromium is an essential mineral that contributes to the normal metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. Chromium also supports the biological process responsible for maintaining normal blood sugar levels. Inorganically bound chromium has low bioavailability in the body. The effectiveness of a chromium supplement is determined by how efficiently the nutrient is absorbed by the body. From FTG to cromodulin
For many years, chromium was thought to be part of a substance called GTF (Glucose Tolerance Factor). GTF, along with chromium, was believed to be composed of B vitamins, niacin, and three amino acids. The GTF theory was only partially supported, and the existence of a specific GTF molecule in the body was never proven.
However, more recently, the existence of a unique chromium-binding molecule called chromodulin has been revealed, which is slightly different from FTG but shares the same characteristics. Thus, when we refer to chromodulin instead of FTG, we are referring to the same benefits.
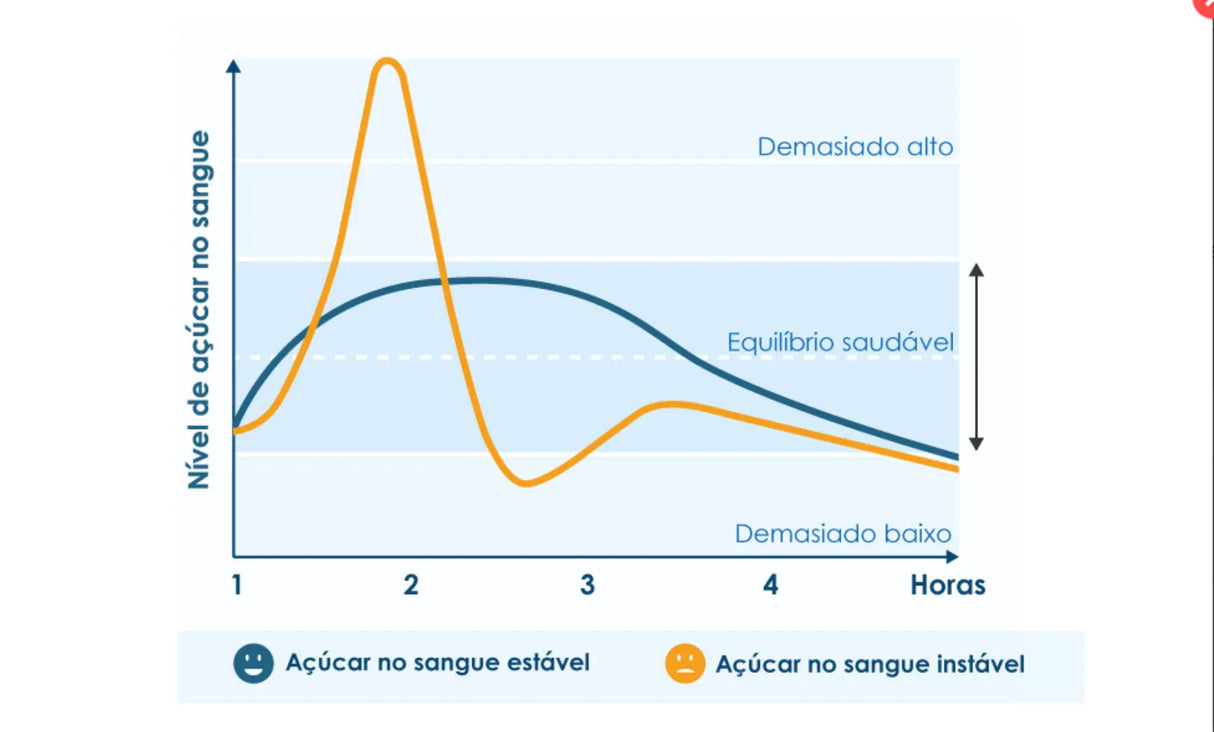
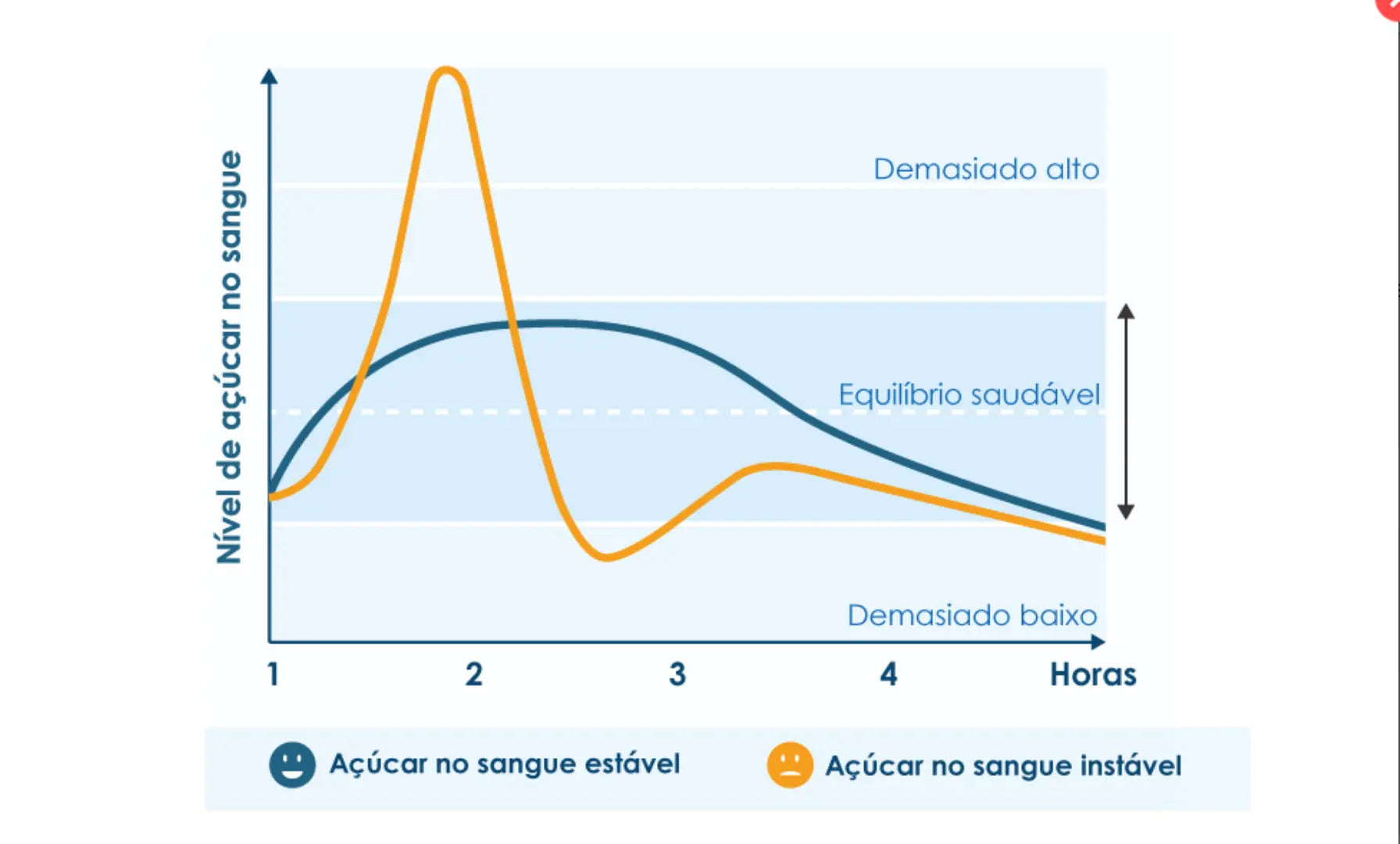
The body's chromium reserves are approximately 4 to 6 mg. As we age, chromium concentrations in various tissues can significantly decrease. Eating a sweet treat may provide temporary relief, due to the sugar that provides immediate energy, but the effect soon disappears. In the long term, these cravings for sweets can have a negative effect on weight. A product like BioActivo Cromo can help the body maintain normal blood sugar levels and prevent this type of situation.
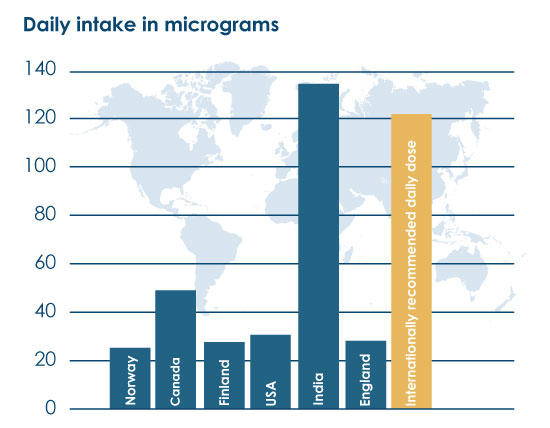
Spices have a high chromium content and this explains why Indians get more of this vital nutrient.
Chromium – a multipurpose mineral
We typically associate chromium with stainless steel, but the form of chromium used for industrial purposes (hexavalent chromium) isn't part of human biochemistry. We rely on chromium in its trivalent form, which is capable of forming three chemical bonds with other atoms.
Analyses of the food consumed by Scandinavians, Englishmen, and Americans show that the average chromium intake is around 30 to 40 µg daily. The EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) recommends a daily intake of 40 µg of chromium, while the WHO (World Health Organization) considers this nutrient safe at doses up to 250 µg.
What foods contain chromium?
Good dietary sources of chromium include:
60 capsules
What is chromium?
Chromium is an essential mineral that contributes to the normal metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. Chromium also supports the biological process responsible for maintaining normal blood sugar levels. Inorganically bound chromium has low bioavailability in the body. The effectiveness of a chromium supplement is determined by how efficiently the nutrient is absorbed by the body. From FTG to cromodulin
For many years, chromium was thought to be part of a substance called GTF (Glucose Tolerance Factor). GTF, along with chromium, was believed to be composed of B vitamins, niacin, and three amino acids. The GTF theory was only partially supported, and the existence of a specific GTF molecule in the body was never proven.
However, more recently, the existence of a unique chromium-binding molecule called chromodulin has been revealed, which is slightly different from FTG but shares the same characteristics. Thus, when we refer to chromodulin instead of FTG, we are referring to the same benefits.
The body's chromium reserves are approximately 4 to 6 mg. As we age, chromium concentrations in various tissues can significantly decrease. Eating a sweet treat may provide temporary relief, due to the sugar that provides immediate energy, but the effect soon disappears. In the long term, these cravings for sweets can have a negative effect on weight. A product like BioActivo Cromo can help the body maintain normal blood sugar levels and prevent this type of situation.

Spices have a high chromium content and this explains why Indians get more of this vital nutrient.
Chromium – a multipurpose mineral
We typically associate chromium with stainless steel, but the form of chromium used for industrial purposes (hexavalent chromium) isn't part of human biochemistry. We rely on chromium in its trivalent form, which is capable of forming three chemical bonds with other atoms.
Analyses of the food consumed by Scandinavians, Englishmen, and Americans show that the average chromium intake is around 30 to 40 µg daily. The EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) recommends a daily intake of 40 µg of chromium, while the WHO (World Health Organization) considers this nutrient safe at doses up to 250 µg.
What foods contain chromium?
Good dietary sources of chromium include:
- seafood
- nuts
- raisins
- meat
- bean
- black pepper
60 capsules
Specifications
Specifications
-
Warnings